Getting Familiar with the Terms
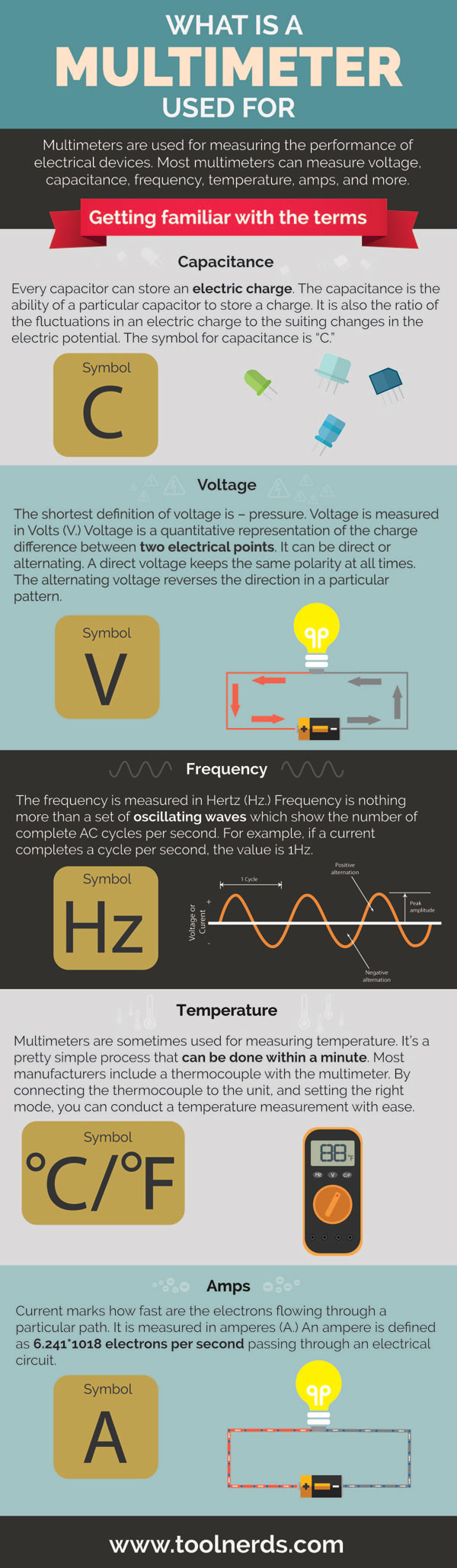
Capacitance
Every capacitor can store an electric charge. The capacitance is the ability of a particular capacitor to store a charge. It is also the ratio of the fluctuations in an electric charge to the suiting changes in the electric potential. The symbol for capacitance is “C.”
Voltage
The shortest definition of voltage is – pressure. Voltage is measured in Volts (V). Voltage is a quantitative representation of the charge difference between two electrical points. It can be direct or alternating. A direct voltage keeps the same polarity at all times. The alternating voltage reverses the direction in a particular pattern.
Frequency
The frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz). Frequency is nothing more than a set of oscillating waves which show the number of complete AC cycles per second. For example, if a current completes a cycle per second, the value is 1Hz.
Temperature
Multimeters are sometimes used for measuring temperature. It’s a pretty simple process that can be done within a minute. Most manufacturers include a thermocouple with the multimeter. By connecting the thermocouple to the unit, and setting the right mode, you can conduct a temperature measurement with ease.
Amps
Current marks how fast are the electrons flowing through a particular path. It is measured in amperes (A). An ampere is defined as 6.241*1018 electrons per second passing through an electrical circuit.










